|
Note: |
|

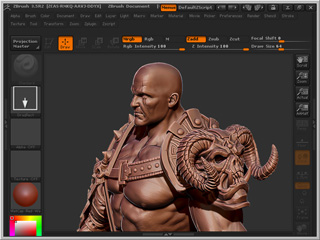
The converted model is also in low-poly status.

|
Note: |
|



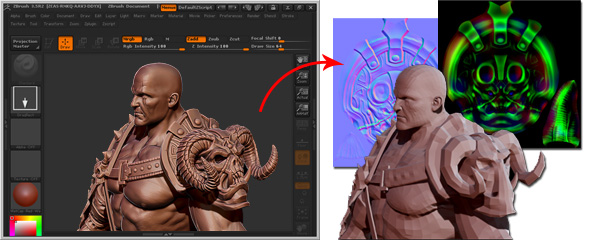
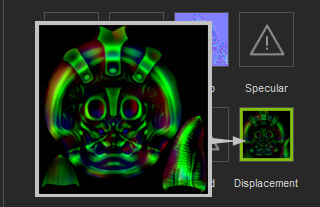
The model without displacement maps is flat and less exquisite.

Vector displacement technology allows artists and developers to start off by
creating detailed models in programs such as zBrush,
Mudbox, or 3D Coat,
and then extract displacement maps to later be applied to a simple geometric shape.
This process is ideal for real-time engines like iClone, and produce results that are incredibly
similar to your actual model. One of the huge advantages of vector displacement is the
ability to produce undercut details on your model. While height
displacement with
grayscale images simply stretches
out geometry, vector displacement produces refined curves and edges, creating an
unparalleled sense of detail to your model.
View the Video


|
Note: |
|





|
Note: |
|



