About Materials
The most import part in the PBR Substance for the clothes and accessories is the Material. A PBR Substance contains up to 7 materials.
These materials are the essential elements for the clothes and accessories, and are portioned out by Color ID in the Mesh Data item. Without a Color ID map, the graph resorts to the Base Material and it is designated with pure black in the Color ID texture.

|
|
|
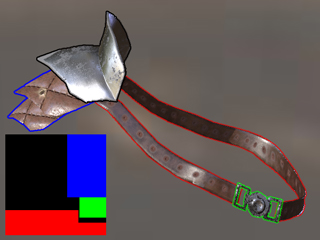
The object is assigned with three materials. These materials are applied onto the object demarcated by the Color ID map. |
Load different Color ID map to change the amount of the materials and the deployment of the materials. |
The materials will be baked as the sources of the channels for the material applied to the clothes and accessories.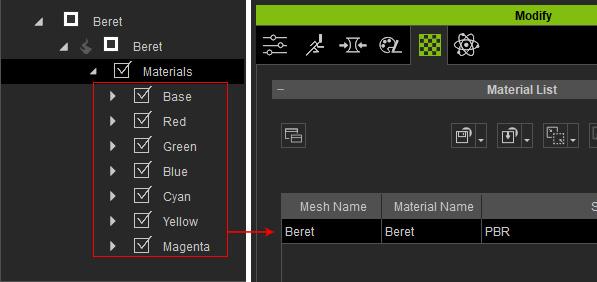
Structure in Each Material
The UI for the individual materials: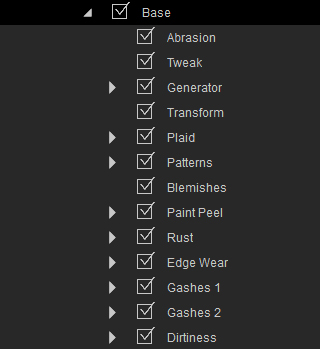
These nodes are divided into three main groups: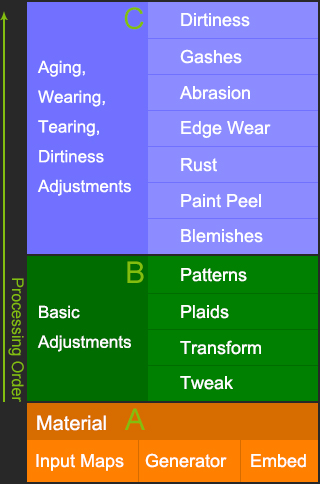
A. Underlying Material Settings:

- Material / Base (or Red, Green, Blue, Cyan, Yellow and Magenta):
In this section, by selecting the Material Type, you are able to determine if you want to set the the underlying material
from scratch, by generator, or
with embedded templates.
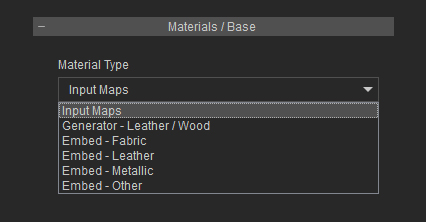
Input Maps
Select Input Maps to load custom textures into different channels in order to create material from scratch.
Generator
Select Generator - Leather / Wood to procedurally create leather or wood texture to the material.
Embed
Select Embed - Fabric, Embed - Leather, Embed - Metallic or Embed - Other to load embedded textures to the material.
 Note:
Note:- Please also refer to the Material Type section for more information.
- In this section, the Base, Red, Green, Blue, Cyan, Yellow or Magenta are represented by "*" sign.
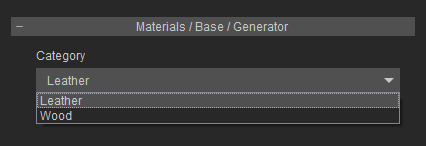
- Material / * / Generator: If you select the Generator - Leather / Wood from the Material Type drop-down list, then you can determine the
material to be Leather or Wood in this section.
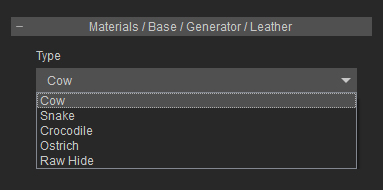
- Material / * / Generator / Leather (or Wood): You can first choose the leather types with drop-down list in this section and do the further
modification for the leather and wood.
 Note:
Note:Please refer to the Using Generator section for more information.
B. Material Basic Adjustments:
- Material / * / Tweak: The Tweak is a material channel superset that is used to modify the input channels and output the results.
When it is switched on, the material do not undergo changes. Use it to modify the color, normal intensity, emissive, roughness
, etc. on the material.


- Material / * / Transform: It is a superset modifier that seamlessly manipulates the UV dimensions of the input channels. Material transform
only influences input maps, generators, and
embed textures.


- Material / * / Plaid: It is a material enhancer that can be used to create crisscrossed horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colors
such as the Scottish Tartan. It can also be modified to create stripes by re-aligning or taking out perpendicular facing stripes
to create patterns like the French Breton Stripes. Plaid can also be applied in other creative ways like making the crevices in
wood planks.


- Material / * / Patterns: All materials share the use of 3 pattern generators that lie outside of the material group.
To control how each one of the patterns are displayed, the patterns control offers adjustments for the way that the 3 patterns are fed into the graph.
The proper operation is to adjust the pattern generators on the parent level then enable and adjust how it is received by modifying the material patterns.


 Note:
Note:The use of Patterns are slightly different from the use of the other settings for the material. Please refer to the Using Generator section for more information.
C. Aging, Wearing, Tearing, and Dirtiness Adjustments:
- Materials / * / Blemishes: It is an exclusively physically based rendering effect that gives metallic surfaces its age and characteristics.
Metallic surfaces, in reality, is rarely perfect, therefore blemishes offer a great way to make natural looking metals. Blemishes are comprised of
3 main components:

- Speckling: the tiny spots of discoloration caused by formations of air bubbles from the cooling of the liquid metal.
- Streaks: thin and long single directional fine lines caused by machining and extrusion.
- Specks: the medium to large spots of discoloration caused by impurities in the metal.
- Materials / * / Paint Peel: Paint peel can be used in a usual way or layering paint on top of the material underneath.
Or it can be used to appear as if the material itself is peeling with the material underneath derived from the paint peel.
When you activate the Paint Peel effect, you can determine the paint peel types with the drop-down list: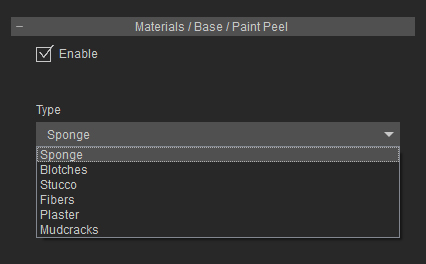



Sponge
Blotches
Stucco



Fibers
Plaster
Mudcracks
- Materials / * / Rust: Material rust can be used to simulate metallic rusting, copper verdigris,
or produce effects that deviate widely from its intended usage such as another glorified dirt generator,
burn marks, etc. Rust is composed of 3 main components:
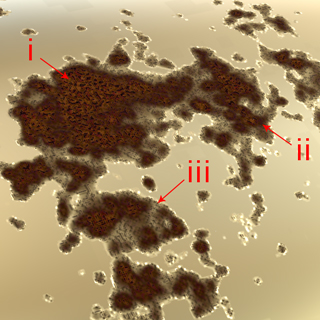
- Spots: the result of oxidation with the impurities that lie within the metal, which are tiny in size.
- Edges: the boundaries of the rust that mark regions still in the incomplete process of oxidation.
- Ring: the outer boundaries of the rust that mark regions that are undergoing the process of oxidation.


- Materials / * / Edge Wear: Edge wear is the effect of an object rubbing against other rough surfaces and in turn having it's
protruding edges being scraped off. It relies on the World Space Normal map in the Mesh Data set, without it,
the edge wear effect will not appear when turned on.


- Materials / * / Gashes: Gashes simulate the look of surface damage by providing some common surface level damage types.
Every 1 of the 7 materials support up to 2 gashes.
When you activate the Gashes effect, you can determine the types with the drop-down list: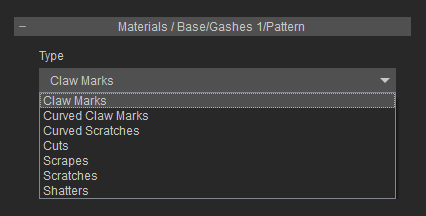



Claw Marks
Curved Claw Marks
Curved Scratches



Cuts
Scrapes
Scratches

Shatters
- Materials / * / Dirtiness: Dirtiness resembles that of stains rather than dirt due to its flat nature.
Dirt placement is generated randomly and based on the Ambient Occlusion map in the Mesh Data set.


